Building Self-Confidence Through Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: Strategies That Work
Have you ever noticed those intrusive thoughts popping up before something important? You’re about to give a speech or go on a first date, and those self-doubting thoughts creep in: “What if I make a fool of myself?” or “Do I really think I’m good enough for this?” Self-doubt, second-guessing your abilities even when you logically know you’re capable, and lack of self-confidence can affect nearly every area of your life, from career advancement to relationships and even daily decision-making.
Although incredibly frustrating and disheartening, low self-confidence is something you can work to change over time.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for self-confidence is an effective, evidence-based approach for helping people build self-confidence and self-esteem. By addressing thoughts and behaviors that fuel self-doubt, CBT helps you challenge limiting beliefs, build awareness of your current thought patterns, practice new ways of thinking, and gradually build confidence. For those who want to dive even deeper into therapy for confidence, this blog offers practical strategies for finding your voice and thriving in relationships and work.
Understanding Self-Confidence and Its Challenges
Self-confidence is your belief in your abilities and judgment. It’s the inner assurance that helps you believe in your capacity to accomplish your goals, feel a sense of control over your life, and navigate challenges and setbacks. Many people struggle with low self-confidence, which can show up as self-doubt, nervousness, fear of failure, or a pervasive sense of inadequacy.
Several factors can contribute to low self-confidence:
Past experiences: Failures or criticism in the past that you’ve internalized and generalized may shape how you view your abilities today.
Negative self-talk: How we talk to ourselves matters. An inner voice that persistently doubts your abilities reinforces feelings of incompetence.
Social comparisons: It’s easy to compare the worst parts of ourselves to the best parts of others without realizing it, often leading to feelings of inferiority.
Cognitive distortions: Irrational, negative thought patterns such as catastrophizing or overgeneralizing can produce or exacerbate fear, anxiety, and depression.
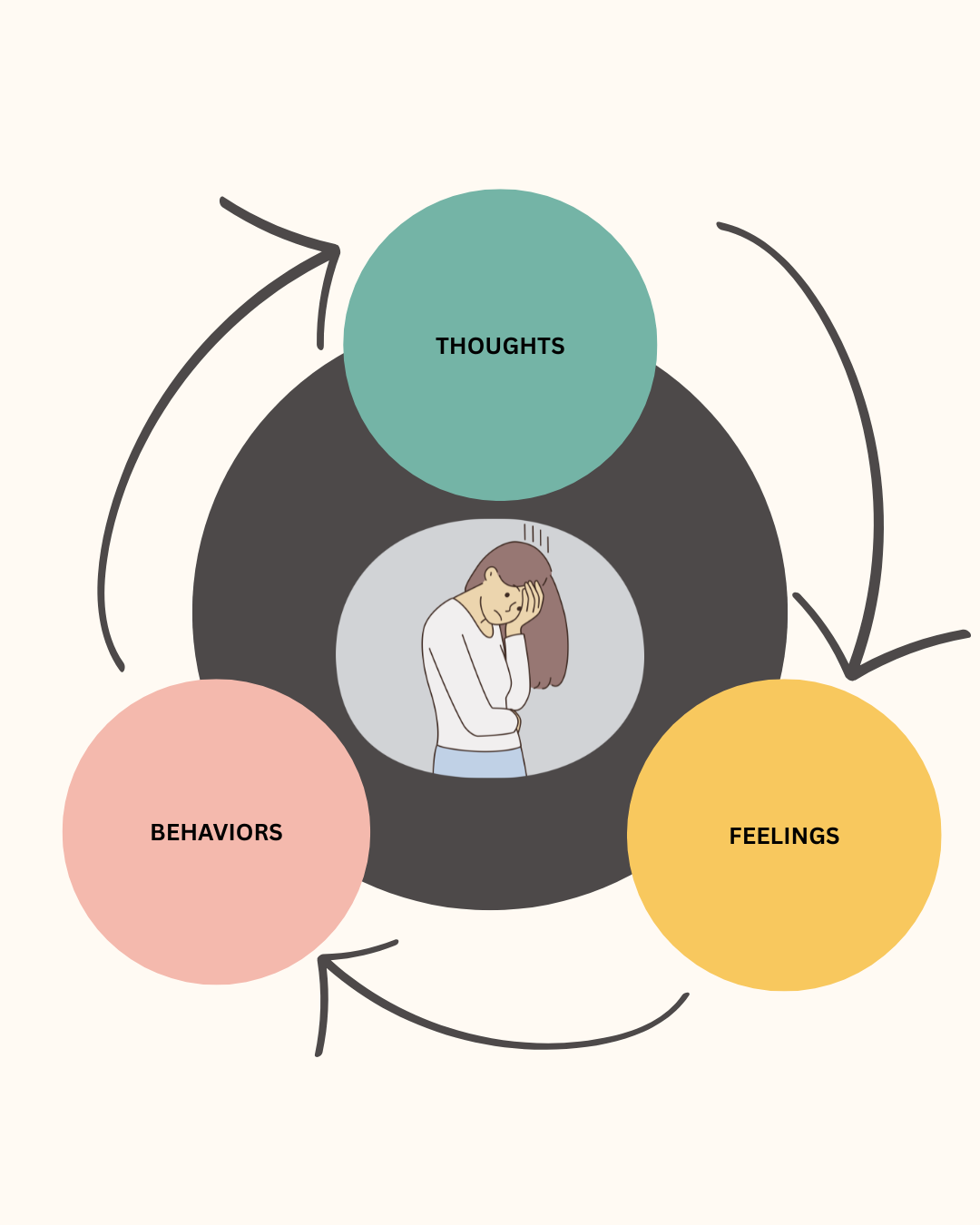
These factors often work together, creating a cycle where negative thoughts generate negative emotions and behaviors, further eroding self-confidence. Recognizing and addressing these patterns is central to building lasting self-esteem.
What is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Self-Confidence?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a type of talk therapy that helps people understand how thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected. By working to identify and change unhelpful thoughts and behaviors, CBT helps improve emotional wellbeing and build self-confidence.
CBT can support self-confidence by:
Identifying negative thoughts: Recognizing and challenging self-defeating beliefs and cognitive distortions.
Reframing cognitions: Replacing irrational or unhelpful thoughts with more balanced, realistic ones.
Developing coping strategies: Learning practical skills to manage anxiety, fear, and self-doubt.
Building belief in yourself: Focusing on positive outcomes and giving yourself reinforcement helps you trust your ability to handle challenges.
Research supports the effectiveness of CBT in improving self-esteem and confidence. It is a valuable tool for understanding how your beliefs and actions affect your mental health and self-perception.
How CBT Addresses Confidence Issues
CBT tackles confidence issues by targeting the thought patterns that contribute to low self-esteem.
Identifying and Challenging Negative Thoughts
The first step is becoming aware of automatic thoughts. Frequently negative thoughts, like “I’m not good enough” or “I’ll never be able to do this,” can undermine your confidence. Once identified, these thoughts can be challenged. Are they accurate? Fair? Can you replace them with more realistic alternatives? A therapist can guide you through this process.
Cognitive Restructuring
Cognitive restructuring involves modifying negative beliefs. For instance, “I’ll never be able to do this” might be reframed as: “This is a difficult task, but I’ve successfully handled challenges before and can learn from this experience.” This shifts your perspective from deterministic to growth-oriented while remaining true to your experience.
Behavioral Activation
Engaging in activities that you are skilled at and that promote well-being reinforces positive self-beliefs. Set small, achievable goals in areas you feel confident in. For example, if you enjoy running, you might aim to run a bit faster or farther, gradually increasing the challenge. Success in activities you already enjoy strengthens self-worth and confidence.
Exposure to Fearful Situations
Gradual exposure to situations that trigger self-doubt helps desensitize fear and build resilience. Facing fears in a controlled, incremental way, often with a therapist’s support, reduces anxiety and increases confidence over time.
Developing Self-Compassion
Self-compassion is integral to confidence. CBT encourages treating yourself with kindness and understanding, especially during moments of failure or difficulty. Rather than harsh self-criticism, you learn to support yourself as you would a friend.
Practical CBT Strategies to Build Self-Confidence
Outside of therapy sessions, several CBT techniques can further enhance self-confidence:
Thought Records: Track negative thoughts in a journal and challenge them with evidence-based reasoning. Structured thought logs can be found online or provided by a therapist.
Affirmations: Use positive statements that feel believable to reinforce self-worth and ability.
Visualization: Imagine yourself succeeding, handling difficult conversations confidently, or completing challenging tasks.
Mindfulness: Practice mindfulness to stay present and reduce anxiety.
Using these strategies alongside cognitive behavioral therapy for self-confidence can improve self-trust, self-worth, and overall mental well-being.
The Role of a Therapist in CBT for Self-Confidence
Working with a trained therapist is essential when applying CBT strategies. Challenging beliefs or confronting fears on your own, without guidance, can sometimes exacerbate self-doubt. A therapist ensures you approach these techniques in a safe, effective way.
Therapists provide:
Personalized Treatment Plans: Tailored interventions based on your needs and goals.
Guidance and Support: Help navigating challenges and setbacks.
Accountability: Regular sessions to monitor progress and adjust strategies.
Skill Development: Teaching coping strategies to manage stress and anxiety.
It’s important to note that some therapists are specifically trained in CBT and use it as their primary modality, while others, like me, incorporate CBT as part of a broader therapeutic process. Both approaches can be highly effective. Ultimately, it’s up to each client to determine which approach feels most helpful and aligned with their goals.
Even small steps toward self-confidence can feel daunting alone; a therapist offers structure, support, and encouragement along the journey.
Self-confidence is fluid. Everyone experiences highs and lows, and building confidence is a process. It involves commitment, recognition and shifting of thought patterns, practice of coping strategies, and reinforcement of positive behaviors. Cognitive behavioral therapy for self-confidence offers a structured, evidence-based approach to developing self-esteem, resilience, and empowerment.
With dedication and the right strategies, you can gradually overcome self-doubt, trust in your abilities, and cultivate a more confident, fulfilling life.
If you are in Colorado and want to talk more about how CBT can be one therapeutic approach to help you change your thought patterns and build self-confidence, reach out today.